Summary
- High-quality image reconstruction technology for CT with fewer projections (sparse view CT).
- Suppresses noise artifacts typical in sparse view CT, achieving image quality comparable to that of conventional CT.
- Image reconstruction is possible with 1/10 to 1/100 of the iterative calculations compared to conventional reconstruction techniques (FISTA method).
- Seeking corporate partners interested in adopting this technology into CT systems.
Technology Overview & Background
Sparse-view CT is a scanning technique that reduces the number of X-ray projections, offering significant advantages such as lower radiation exposure and shorter scan times. However, fewer projections often lead to artifacts, especially streak artifacts, resulting in poor image quality.
To address this, compressed sensing (CS)-based reconstruction algorithms have been developed. While effective in reducing streak artifacts, these methods can oversmooth the image, causing the loss of fine density variations necessary for accurate diagnostics.
Professor Hiroyuki Kudo of the University of Tsukuba has developed a novel reconstruction algorithm that dramatically improves image quality and reduces computational load. While based on compressed sensing principles, the algorithm introduces the following innovations:
1.Improved Regularization
Traditional regularization methods such as L1-norm and Total Variation (TV) are extended by combining them and incorporating nonlinear smoothing filters (e.g., non-local means filters). Additionally, the algorithm introduces second-order derivative terms into the regularization, enabling the comparison of pixel values over longer distances within the image. This suppresses the loss of fine contrast caused by TV regularization alone, yielding smoother and more natural reconstructions even in sparse view CT.
2.Faster Convergence
Conventional methods like FISTA (Fast Iterative Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm) require a large number of iterations, increasing computational time and cost. The new algorithm proposed by Professor Kudo drastically reduces the number of iterations by boldly rewriting the minimization problem solved in compressed sensing reconstruction. The method, in essence, involves introducing the FBP method—which enables reconstruction without iterative calculations—into compressed sensing and using projection data in parts during iterative processing. As a result, the number of iterations required to obtain equivalent reconstructed images has been drastically reduced to 1/10 to 1/100 of that in the FISTA method (see figure below).
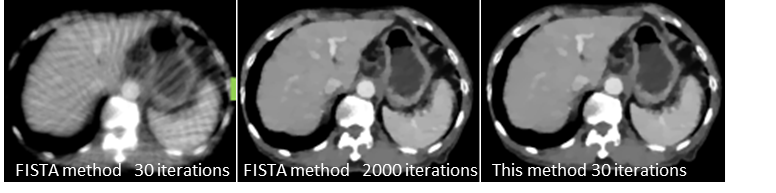 |
Comparison of convergence speed in sparse view CT (number of projection directions: 64)
Researchers & Academic Institution
Hiroyuki Kudo, PhD (Professor, Faculty of Engineering, Tsukuba University, Japan), et al.
Expectations
We are seeking companies interested in incorporating this technology into their CT systems—whether for medical, dental, or industrial non-destructive testing applications.
By utilizing this high-speed, low-dose, and high-quality image reconstruction technology from the University of Tsukuba, you can enhance your CT system’s performance. If you are interested in further technical details, please contact us. We offer opportunities for direct meetings with the developer and can discuss paid contracts for sample programs and technical instruction.
In addition to the sparse view CT, we also offer advanced reconstruction techniques for interior CT and machine learning-based reconstruction. Please refer to the links below for more information:
- A New Proposal for Low-Dose, High-Accuracy X-ray CT
- Deep Learning-Based Compressed Sensing Image Reconstruction Technology
Project ID:DA-02355b


