Advantages
- Some anti-CKAP4 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) obtained
- Tumor suppressing effects were found for both pancreatic and lung cancer in mouse xenograft model by using anti-CKAP4 mAbs
Technology
Lung, pancreatic and some other cancer treatment by using anti-CKAP4 mAb. According to the fact that DKK1/CKAP4 signaling promotes cancer cell proliferation, highly tumor suppressing effects are expected at cancer describe above harboring with DKK1 over-expression and high expression of CKAP4 on its cell membrane.
Background
Dickkopf1 (DKK1) is a secretory protein that antagonizes oncogenic Wnt signaling by binding to the Wnt coreceptor low density lipoprotein receptor–related protein 6 (LRP6). It has been shown to suppress tumorigenesis in some cancer cells, however, it is also up-regulated in many types of cancer and associated with poor prognosis. Wnt-independent mechanisms by which DKK1 promotes cancer cell proliferation are not well understood.
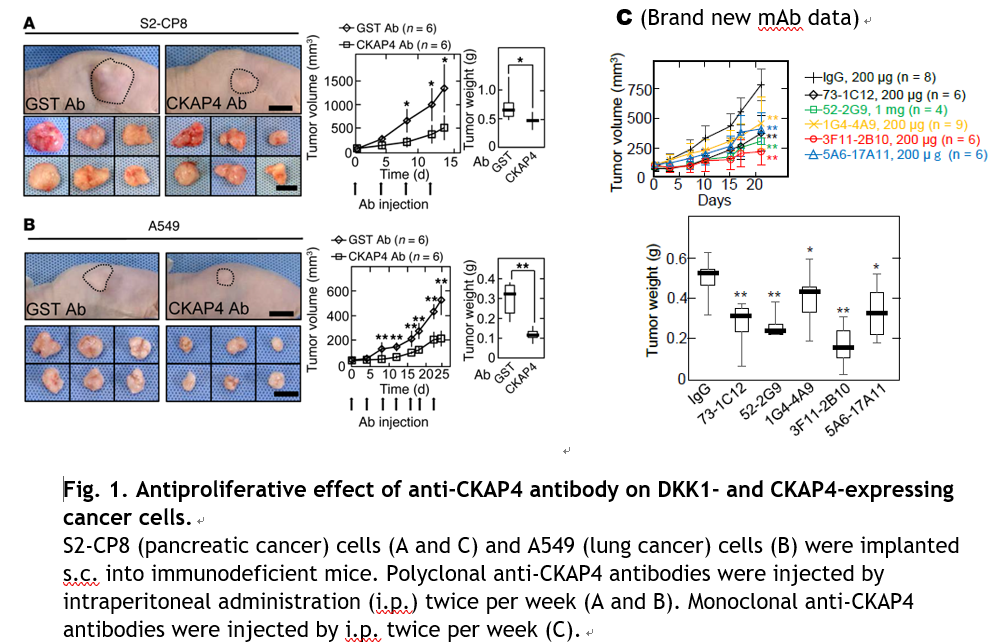
In this study, researchers identified that cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (CKAP4) is a novel DKK1-binding protein by using mass spectrometry analyses and immune sedimentation, then found that it becomes a new therapeutic target. CKAP4 was detected in tumor lesions of 66–74% of pancreatic and lung cancer cases. The researchers also demonstrated that DKK1 interacts with CKAP4 to promote activation of AKT, and CKAP4 specifically regulate tumor cell proliferation by DKK1. They also showed that suppressing of CKAP4 gene expression or polyclonal antibodies inhibit proliferation of tumor cells.
Data
- Researchers specified DKK1 binding region on CKAP4, designed and obtained some anti-CKAP4 mAbs against on the C-terminal region epitopes of CKAP4 which are highly homologous between mice and human.
- The role of CKAP4 expression in tumorigenesis in vivo was investigated by s.c. implantation of pancreatic or lung cancer cells into the flanks of immunodeficient mice. Anti-CKAP4 antibodies inhibited proliferation of these cancer cells, and the volumes and weights of the xenograft tumors decreased.
Researchers
Dr. Akira Kikuchi, et al. (Professor, The University of Osaka, Japan.)
Publications
- H. Kimura, A. Kikuchi, et al., J. Clin. Invest. 2016;126(7): 2689–2705.
DOI: 10.1172/JCI84658. - N. Shinno, A. Kikuchi, et al., Oncogene (2018) 37: 3471–3484.
DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0179-2. - C. Kajiwara, A. Kikuchi, et al., Cancer Res. pii: canres.1749.2018.
DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1749. - H. Kimura, A. Kikuchi, et al., Clin. Cancer Res., January 4 2019.
DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2124.
Patents
- PCT/JP2016/052485 (National phases: CA, CN, EP, US, JP-DIV and Issued: JP)
- PCT/JP2018/035719 (Before national phase)
Expectations
We are looking for a pharmaceutical company entering collaboration with the researchers to develop and commercialize this technology further by patent licensing. We also appreciate any consideration of collaborative/supportive research or exclusive/non-exclusive evaluation for defined period (set up for options).
Product No: TP-00481