Advantage
- Potent antiviral activity against a wide range of virus species, including Dengue virus, Zika virus, and SARS-CoV-2.
- The compound prevents viral replication via the inhibition of virus-dependent RNA polymerase
Current Stage and Key Data
Lead compound optimization
- The compound demonstrated in vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, two types of human coronaviruses (strain 229E and OC43), Dengue virus, Zika virus, yellow fever virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, and West Nile virus.
- The compound improved survival rate and inhibited viral replication in Dengue virus infection model mice and SARS-Cov2 infection model mice.
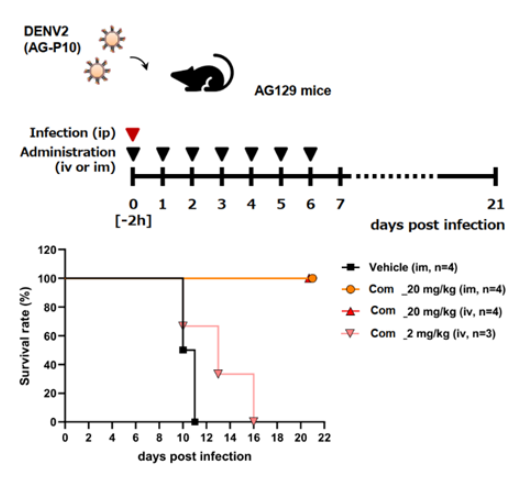 |
Partnering Model
Seeking partner companies to work on optimizing this compound, as well as conducting non-clinical and clinical trials.
- Potential partners: Pharmaceutical/Biotech companies focused on developing drugs to treat viral infections or NTDs.
Background
We have identified new compounds by screening nucleic acid antimetabolites with antiviral activity using a nucleic acid-like compound library in owned by the Research and Education Center for Drug Discovery Science, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hokkaido University. The new compounds exhibited high antiviral activity against positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses such as coronavirus and flavivirus.
Patents
- Patent pending : US, EP, JP, CN, KR, SG, CA
Principal Investigator
Akira Matsuda (Faculty of Pharmaceutical Science, Hokkaido University), et al.
Project ID:BK-04122b


