Advantages
Application
- For Clinical Decisions
- Drug Selection Navigation: Simulates the effectiveness of different drug candidates for a specific patient, predicting which therapy will offer the most benefit and explaining the reasoning behind the choice.
- Surgical Timing Optimization: Helps resolve clinical dilemmas by simulating outcomes for different treatment paths. For high-risk cases like infective endocarditis, it can predict the prognosis for both early and delayed surgery to guide the optimal strategy.
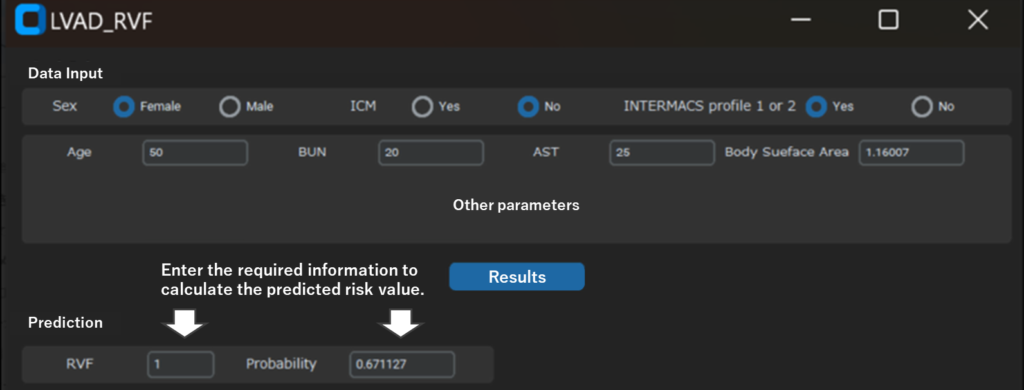
- Pre-Surgery Simulation: Predicts the risk of post-LVAD Right Ventricular Failure (RVF) and simulates how pre-operative interventions (e.g., diuretics, inotropes) can lower that specific risk, thereby optimizing patient management before surgery.
- For Hospital Management
- ICU Bed Management: Aggregates individual patient predictions (e.g., risk of prolonged intubation) to create a hospital-wide forecast of ICU bed demand. This helps optimize resource allocation and bed control.
- Discharge Support: Identifies patients at high risk for prolonged hospitalization or complications. These alerts care about teams sooner, enabling proactive planning for complex discharge needs like rehabilitation or home nursing.
- For Pharmaceutical R&D
- Drug Responder Discovery: Identifies which patient types respond best to specific drugs by analyzing existing clinical data. This can help optimize clinical trial design and uncover new potential patient segments for existing medications.
Technology Overview & Background
In modern medicine, there is a growing need for personalized treatment, yet it is increasingly difficult for physicians to determine the optimal therapy due to complex patient conditions and diverse responses to treatment. This is especially true in cardiovascular medicine, where predicting critical outcomes—such as Right Ventricular Failure (RVF) after Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD) surgery or mortality after Infective Endocarditis (IE) surgery—is a major challenge. While AI is a promising tool, its adoption has been hindered by the “black box problem,” where the AI’s reasoning is unclear, making it difficult for clinicians to trust.
This system was developed to solve these problems. It is an “explainable AI” (XAI) tool built on a foundation of high-quality, real-world clinical data from Osaka University and the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center. By analyzing this data, AI achieves superior accuracy in predicting major adverse events. Crucially, it uses a technique called SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) to visualize the specific factors driving each prediction. This transparency allows physicians to understand the rationale, medically validate the results, and confidently apply them to deliver truly personalized care.
Data
- Post-LVAD RVF Prediction: Achieved a high accuracy of AUC 0.89, significantly outperforming the conventional score (AUC 0.65).
- Post-IE Mortality Prediction: Demonstrated excellent performance with an AUC of 0.92 and 97% overall accuracy.
Patent(s)
Patent(s) Pending (Not yet published)
Principal Investigator & Academic Institution
Dr. Takaaki Samura, Dr. Shigeru Miyagawa (Osaka University, Graduate School of Medicine)
Expectations
We are seeking partners to commercialize this technology as a Program as a Medical Device (SaMD). We are looking for medical device or AI companies with strengths in the cardiovascular or post-operative management fields.
We offer flexible collaborations (joint research or licensing) and can provide the completed AI prototype, the underlying clinical dataset, and expert knowledge from the inventors. Please contact us to discuss this opportunity.
Project ID:WL-05232