Advantage and Core Benefit
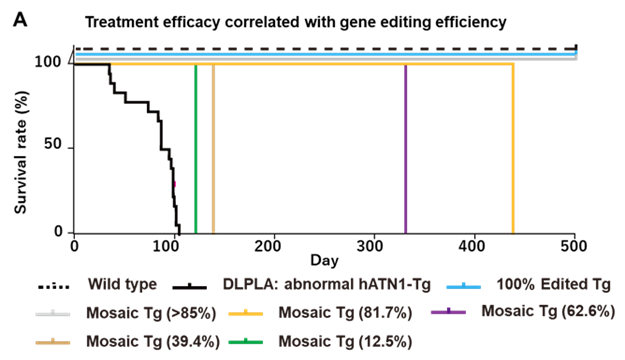
- Efficacy Confirmed in DRPLA Model Mice: Complete suppression of disease onset was achieved in mice with 100% editing of the ATN1 gene. Even in mosaic editing cases (12.5%–92.8%), therapeutic effects were observed in proportion to the editing efficiency.
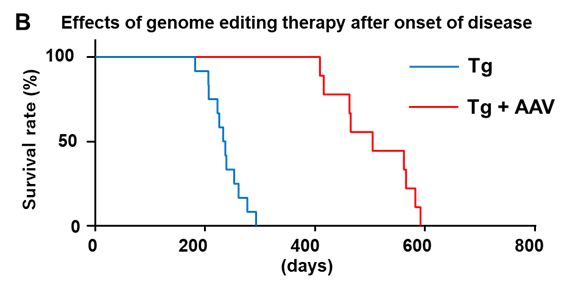
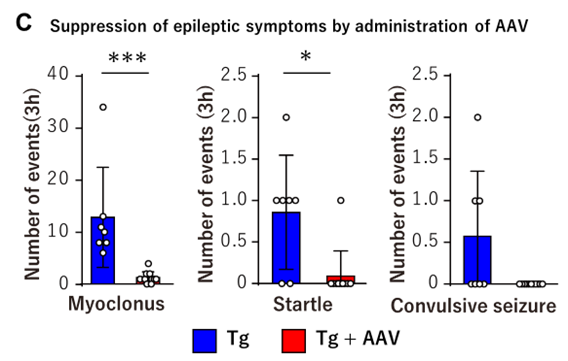
- Post-Onset Treatment Feasible: Intravenous administration of CRISPR/Cas9 constructs using AAV-PHP.eB vectors was effective even after disease onset, demonstrating potential for therapeutic intervention at symptomatic stages.
Background and Technology
Polyglutamine diseases are a group of neurodegenerative disorders caused by abnormal expansion of CAG repeat sequences in specific genes. One such disease is Dentatorubral-Pallidoluysian Atrophy (DRPLA), caused by CAG repeat expansion in the ATN1 gene. In children, DRPLA presents with ataxia, epilepsy, and cognitive decline; in adults, it is characterized by progressive ataxia and dementia.
Although antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) therapies have been under development, they face limitations such as poor delivery to the central nervous system (CNS), limited durability, the need for lifelong repeated administration, and inability to directly modify the mutant gene.
To overcome these limitations, the inventors developed a genome editing strategy using CRISPR/Cas9 to introduce a frameshift mutation upstream of the CAG repeat, thereby inducing a premature stop codon and halting translation of the toxic polyglutamine protein. In DRPLA model mice carrying the human mutant ATN1 gene, complete suppression of disease onset was observed in 100% edited mice. Mosaic edited mice also showed improvements proportional to editing rates. Furthermore, the post-onset administration of the AAV vector carrying the CRISPR/Cas9 construct significantly suppressed disease progression, including a near-complete suppression of epileptic seizures.
 |
 |
 |
Patent & Publication
Patent pending (unpublished)
Researcher
Dr. Osamu Onodera, Dr. Taisuke Kato (Niigata University)
Expectations
Genome Editing Therapeutics Companies: We welcome collaborations for clinical development of genome editing-based therapeutics through licensing of this invention.
Delivery Technology Developers (e.g., AAV, CRISPR-Cas9): We aim to establish candidate therapeutic products by integrating our CRISPR/Cas9 constructs with industry-developed delivery platforms and proceed to efficacy validation and clinical development through joint research.
Resources Available for Evaluation and Co-Development: Genome editing constructs and DRPLA animal models are available under fee-based Material Transfer Agreements (MTAs) for technical evaluation or development purposes.
Project ID:WL-05289


