Experimental Data Summary
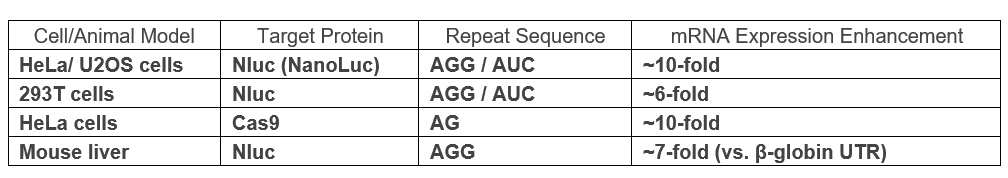 |
Advantage and Core Benefit
- Simple replacement of the β-globin-derived 5’UTR with a synthetic repeat sequence yields over 5-fold enhancement in protein expression.
- Various repeat sequence designs have been validated, enabling customization for specific genes-of-interest (GOIs) and target tissues.
- Further enhancement is possible by combining with mRNA stabilization strategies such as OAS3 (2′-5′-Oligoadenylate Synthetase 3) inhibition.
Background and Technology
mRNA therapeutics have emerged as a key modality in drug development, especially following the success of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. However, low intracellular translation efficiency remains a critical bottleneck.
Through studies on mRNA translation, the inventors identified that β-globin-derived 5’UTR sequences have limited contribution to mRNA expression. To address this, they systematically replaced these sequences with defined di- and trinucleotide repeat motifs. Among these, the AGG repeat (50 nt) introduced into the 5’UTR significantly improved protein expression, achieving up to a 7-fold increase in mouse liver and up to a 10-fold increase in various cells compared to β-globin UTR.
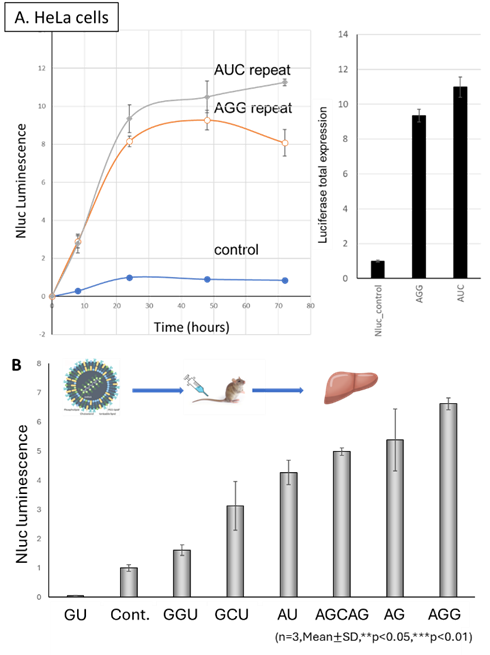
Data
- Sustained Expression: Nluc expression from AGG- or AUC-repeat-containing mRNA persisted for over 80 hours in HeLa cells and 50 hours in 293T cells.
- In Vivo Validation: mRNA-LNPs incorporating 5’UTR repeat sequences administered intravenously in mice led to a 7-fold increase in liver Nluc expression over β-globin UTR controls.
 |
Patent & Publication
Patent Pending (unpublished)
Researcher
Prof. Shinichi Hoshino (Nagoya City University)
Expectations
Vectors incorporating the repeat sequence-modified 5’UTRs are available under a paid MTA (Material Transfer Agreement) for evaluation studies.
We seek collaborative opportunities with the following types of companies:
Pharmaceutical/Biotech: For mRNA drug and RNA vaccine development with enhanced translation efficiency.
DDS Platform Developers: For integration with mRNA delivery systems.
Gene Editing Companies: To improve CRISPR-Cas9 expression and editing efficiency.
Cell Therapy Developers: For enhanced intracellular protein expression, including efficient iPS cell generation.
R&D Divisions: As a translational tool for internal mRNA research.
Project ID:WL-04874


