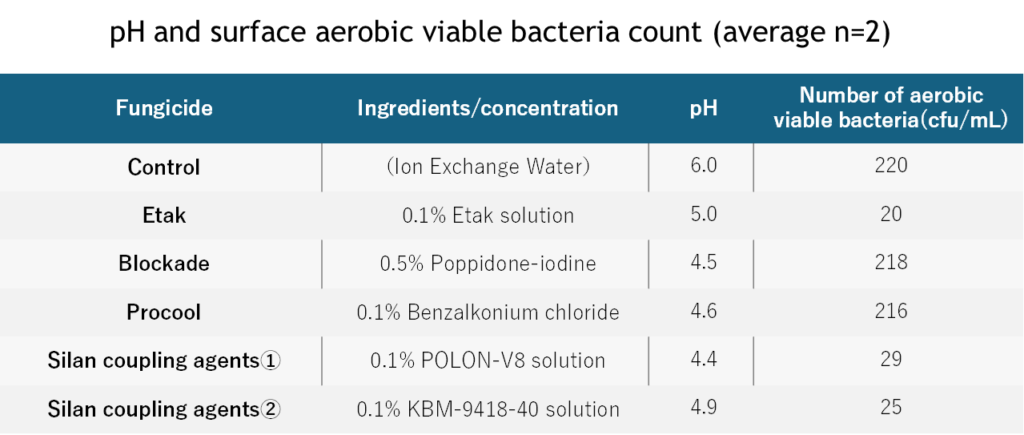
Advantages
- Demonstrated high antimicrobial activity compared to prior fungicides
- Membrane-forming ability of quaternary ammonium salts promises sustained fungicide performance
- The fields where antibiotic use restrictions raise expectations for an effective solution
Current Stage & Goals
With the worldwide increase in dairy herds, the incidence of infectious diseases, especially bovine mastitis, has been increasing rapidly year by year in recent years. While there is a growing need for treatment of mastitis, as well as for a better environment for raising animals and care during milking and after treatment to prevent new outbreaks, there are growing industry expectations for innovative methods of dealing with the disease, as many countries tighten restrictions on the use of antibiotics.
In this environment, iodine-based disinfectants are used by dairy farmers as a measure to prevent and treat infectious diseases in livestock. While these are effective against bovine mastitis, there are concerns about residues and excessive use can irritate the skin and mucous membranes of animals, causing inflammation and allergic reactions. In addition, although dipping treatment must be applied at each milking to prevent bovine mastitis, it is of limited duration and does not adequately control the infection until the next milking. Therefore, there is a need for an agent that is less harmful to the environment and animals and that maintains its effectiveness in preventing infection.
The inventors focused on the fact that quaternary ammonium salt fungicides are not easily deactivated even in the presence of large amounts of organic matter as a new agent to reduce the risk of disease in livestock, especially bovine mastitis, and in addition, they tested the effectiveness of quaternary ammonium salt coupling agents under the hypothesis that they tend to stay on livestock body surfaces and demonstrated high efficacy. The results were highly effective.
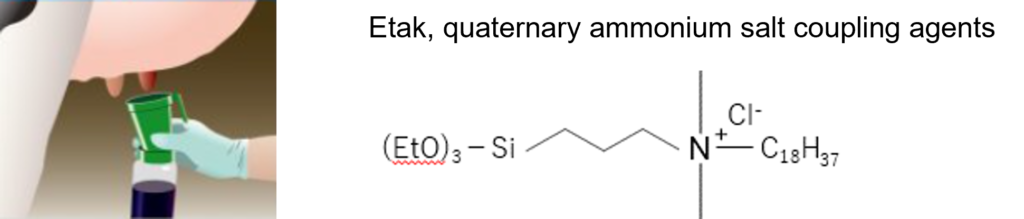 |
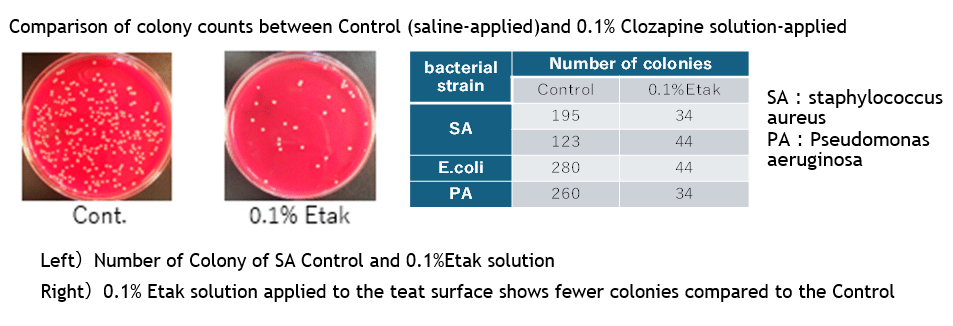
Data
 |
Patent
Pending ; International phase
Applicant
Azabu University
Researcher
Azabu University Department of Veterinary Medicine Professor Kazuhiro Kawai
Okayama University of Science Department of Veterinary Medicine Professor Yasunori Shinozuka
Development Phase
Current stage:
POC for the antimicrobial activity has been completed
Next stage:
1) Demonstration in comparison with prior agents, in dairy animals, and development of optimal usage
2) Obtaining regulatory approval
We are looking for development and collaboration partners for the above. We would be happy to start with a detailed explanation and discussion of the technology.
Project ID: ON-05218