Advantages
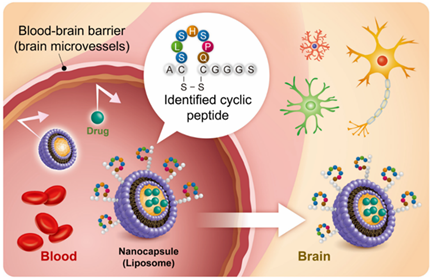
- A short cyclic peptide, composed of seven amino acids linked by a disulfide bond, enhances BBB permeability for macromolecular drugs (e.g., antibodies and nanoparticles).
- Binding to drugs and other modalities can be achieved via non-covalent interactions, covalent conjugation, or genetic fusion.
Technology Overview & Background
One of the biggest challenges in the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) diseases is the efficient delivery of therapeutic drugs to the brain. However, the blood-brain barrier (BBB), the most selective physical barrier between blood and brain, poses a significant obstacle to the transport of many drugs into the brain. This challenge is particularly pronounced for medium- and high-molecular-weight therapeutics, such as antibody-based drugs and nanoparticles, which have limited ability to cross the BBB, thereby restricting their therapeutic efficacy.
In this study, the researchers focused on developing carrier molecules for macromolecur drug delivery to the brain and identified a short cyclic peptide that facilitates BBB penetration, named the SLS peptide (see figure below). The complex formed by conjugating the SLS peptide with a drug exhibited significantly enhanced BBB permeability, leading to a substantial increase in drug migration into the brain parenchyma. The complex formed by conjugating the SLS peptide with a drug exhibited significantly enhanced BBB permeability, leading to a substantial increase in drug migration into the brain parenchyma. Furthermore, liposome and antibody complexes incorporating the SLS peptide can be easily prepared using existing production technologies and established drugs. This technology is expected to make a significant contribution to the brain delivery of medium- and high-molecular-weight therapeutics.
 |
Data
- Using the M13 phage library expressing various candidate peptides, a permeability assay was conducted with hCMEC/D3 cells, a type of human BBB model, to identify the SLS peptide, which enhances the transport of macromolecules across the BBB.
- In a hierarchical spheroid-type human BBB model that closely mimics the morphology of the human BBB, it was confirmed that brain penetration was significantly enhanced for anionic liposomes (150 nm) and monoclonal antibodies (150 kDa) complexed with the SLS peptide.
- In brain permeability evaluation experiments using mice, the SLS peptides was shown to significantly promote migration into the brain parenchyma in combination with multiple antibody drugs (Aducanumab, Trastuzumab) and anionic liposomes.
Publication(s)
Yamaguchi, S. et al., J Control Release. (2020) 321, 744-755.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.03.001
Patent(s)
(JP) 7378046, Issued.
(US) Pending.
Principal Investigator & Academic Institution
Shingo Ito, PhD (Associate Professor, Kumamoto University, Japan)
Expectations
TECH MANAGE is now looking for pharmaceutical companies or start-ups to consider collaborating with Dr. Ito on this invention. A confidentiality agreement (CDA) allows Kumamoto University to provide unpublished data and related know-how. In addition, licensing options can be set up for evaluation of related intellectual property.
Project No.JT-05121


