Development of two RF related technologies for orf137, a CMS gene
1. Generation of new RF lines with mutant genes that function as fertility restoration genes.
2. Identification of DNA markers for the fertility restoration locus in wild species.
Background
Breeding with cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) and fertility restoration (RF) genes has many advantages, including (1) efficient F1 seed production and cost reduction, (2) utilization of hybrid strengths to improve quality and yield, and (3) increased breeding flexibility, which is advantageous from a food security perspective. Tomato is a major agricultural plant with a global production of approximately 186.8 million tons as of 2020, and there is a high need for breeding for yield improvement, disease resistance and environmental adaptability. MSA1 was established as a CMS line in tomato by Nichirei Corporation, and subsequent research identified the mitochondrial gene orf137 as a CMS gene. The restoration of fertility in F1 lines obtained by crossing CMS lines with orf137 with wild species such as S. pimpinellifolium (LA1670) and S. cheesmaniae (LA166) suggests the presence of RF genes, but they have not yet been identified.
A group at the University of Tsukuba and the Kazusa DNA Research Institute has developed two technologies for RF lines of tomato.
Technology 1: Creation of RF lines by mutagenesis
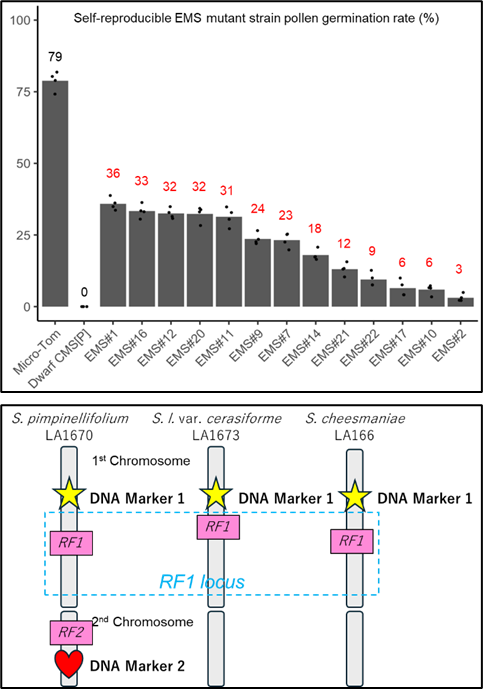
- CMS tomato lines were subjected to mutation induction by EMS, and lines capable of producing self-fertile seeds were selected. Pollen germination rate of 13 lines was up to 36% (upper right figure), and genome analysis identified several mutated genes.
Technology 2: DNA marker identification of RF loci in wild species
- DNA markers were identified for the RF1 locus on chromosome 1 involved in fertility restoration in LA1670, LA166, and S. lycopericum ver. cerasiforme (LA1673), narrowed down to 1.36 Mbps, 1.32 Mbps, and 0.61 Mbps, respectively. In addition, for LA1670, we identified a fertility restoration locus RF2, which differs from RF1, in a region of 9 Mbps on chromosome 2.
 |
Materials
CMS system: MSA1 or Dwarf CMS (Nichirei Foods Corporation, a cooperative company, will be the provider)
RF lineage: EMS#1
Information on DNA markers for wild RF loci
Patent
Pending (Unpublished)
Researcher
Dr. Kenta Shirasawa (Kazusa DNA Research Institute) Dr. Kousuke Kuwabara (University of Tsukuba)
Expectations
We are interested in partnering with seed companies and Agri-tech companies that are interested in using this technology for tomato breeding. If you wish to evaluate for licensing introduction, a time-limited MTA (for a fee) on seeds and DNA markers of the CMS and RF lines listed in Material is available.
Project No.WL-04914


