Advantage and Core Benefit
- High sensitivity and specificity: it has been detected in existing ACPA and RF-negative rheumatoid arthritis patients, suggesting that more RA patients can be accurately diagnosed.
- Potential for early diagnosis: the ability to diagnose RA at an early stage is expected to lead to earlier therapeutic intervention.
- Monitoring of disease activity and assessment of treatment efficacy: it is expected to enable assessment of the efficacy of treatment over time.
Background and Technology
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease that progresses to joint swelling and pain, and then to joint deformity and destruction. The diagnosis of RA is based on a comprehensive assessment of joint symptoms and blood test values. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) against citrullinated peptides are known to be present in RA patients. ACPA, detected by cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP), plays an important role in the diagnosis of RA, but not all patients are positive. In addition, ACPA is difficult to diagnose at an early stage and to monitor treatment response.。
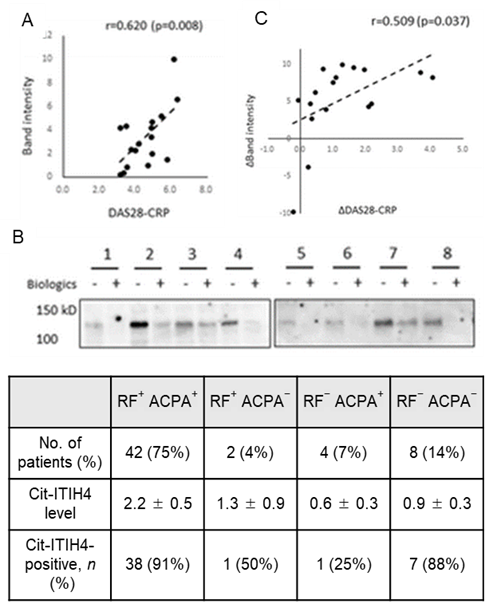
The inventors analyzed citrullinated proteins in sera from their own mouse model of RA (pGPI-induced arthritis mice) and human RA patients and found that in both sera the 438th arginine residue of ITIH4 (Inter alpha trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4) was commonly found to be citrullinated in both sera. This citrullinated ITIH4 (cit-ITIH4) was not detected in healthy individuals or in other autoimmune diseases such as SLE but was detected specifically in RA patients and was further correlated with disease activity. It was also found that this cit-ITIH4 is more abundant in RA synovial fluid and is positive in a form that reflects arthritis and leaks into the blood. In addition, cit-ITIH4 was detected in seven out of eight ACPA-negative and RF-negative patients, which is expected to enable accurate diagnosis in patients who could not be diagnosed by existing serological tests. At present, cit-ITIH4 can be identified by immunoprecipitation, but the aim is to develop an antibody specific for cit-ITIH4 and to develop a new diagnostic technique for RA by detecting cit-ITIH4 using more convenient ELISA and other methods.
Data
- Relationship between serum cit-ITIH4 and RF/ACPA in RA patients (Table). Correlation between cit-ITIH4 levels and DAS28-CRP, a measure of disease activity, in RA patients (n = 17) (A). Western blot analysis in serum samples of RA patients before and 24 weeks after treatment with biologic agents (1-2: abatacept, 3-8: infliximab) (B). Correlation between pre- and post-treatment cit-ITIH4 levels and difference in DAS28-CRP (C).
 |
Patent & Publication
Patent: JP7202010B2, US11774447B2
Paper: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1562-7
Researcher
Dr. Isao Matsumoto (University of Tsukuba)
Current Stage & Expectations
Current Stage: anti-ITIH4 antibody, anti-cit(R438)-ITIH4 antibody have been established and an ELISA system is being attempted.
Expectations to companies: we would like to conduct joint research with companies that develop diagnostic products and license out patents. We are interested not only in collaborating with companies that can jointly construct an ELISA system, but also in developing diagnostics using the company’s own technologies and detection systems, such as mass spectrometry.
Project No.WL-05015


