Advantages
- Using organic redox molecules as mediators is expected to reduce costs.
- By immobilizing enzymes, electrodes, and mediators, a wearable sensor capable of continuous measurement can be realized.
Technology Overview & Background
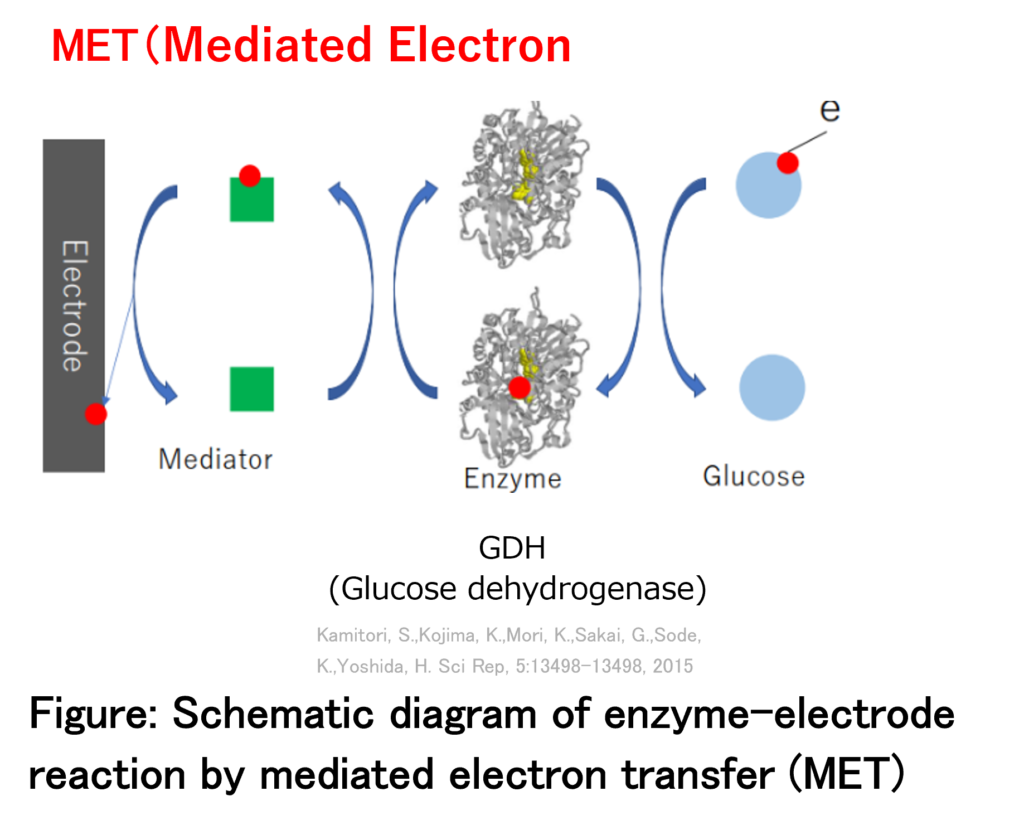
A biosensor uses bio-related molecules for sensing, and in particular electrochemical biosensors measure a combination of electrode reactions and redox reactions of enzymes or microorganisms. They can be made small and lightweight, and their development is being widely pursued. A typical example is the glucose sensor that measures blood glucose levels, and in recent years, CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitoring) sensors that measure blood glucose levels continuously have become popular. Recently, there are hopes for their application to wearable sensors, but there is room for improvement in terms of efficiency, cost, sensitivity, and miniaturization. In particular, the development of an electron transfer mediator between the enzyme and the electrode is important.
By applying this technology to various wearable electrochemical devices such as wearable biofuel cells and biosensors as well as CGM sensors for blood glucose measurement, high performance can be achieved at low cost. It can also be applied to self-powered sensors based on the mechanism of biofuel cells. In addition to continuous monitoring of components contained in sweat and urine, it is expected to be applied to various biochemical testing applications using other enzymes and microorganisms, and it is expected to be used in a wide range of fields, including the medical field, environmental monitoring, and the food industry.
Data
- When the enzyme and phenothiazine-based molecules were bound to a polymer and immobilized on an electrode, the current density due to glucose oxidation increased significantly.
- A higher current density was obtained when the enzyme and electrode were immobilized through chemical bonding using an appropriate crosslinker.
- When a carbon electrode bound to a mediator molecule was used as the anode, a higher output was observed compared to when an electrode without a mediator molecule was used as the anode.
Publication(s)
Morshed J., et al., Biosens Bioelectron. 2023 Jun 15:230:115272.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2023.115272
【DOI】10.1039/D4MH01538J
Patent(s)
JP2023-128505、JP2023-128506、JP2023-176606, unpublished patent.
Principal Investigator & Academic Institution
Seiji Tsujimura, University of Tsukuba, Associate Professor
Expectations
University of Tsukuba is looking for companies that can use this invention to develop wearable or implantable biosensors. It is also expected that this invention can be applied to biofuel cells and the measurement of biomolecules other than glucose. If there are companies that are interested in biofuel cell development or the rapid, low-cost measurement of biomolecules with biosensors, let’s work together to develop this technology.
In addition to disclosing unpublished data by concluding a confidentiality agreement with University of Tsukuba, we also offer meetings with researchers.
Project No.KJ-04798