Advantages
- Expected to be effective in treating cancers resistant to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
- Can be administered both intratumorally and intravenously for effectiveness.
- Anticipated applications extend beyond cancer therapy to include allergic and infectious diseases, where activation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and induction of interferon alpha are beneficial, as well as use as a vaccine adjuvant.
Technology Overview & Background
CpG oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG ODNs) are Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) agonists that induce innate immune responses, including interferon and inflammatory cytokine secretion. CpG ODNs are categorized into several types based on their chemical structure. Type A CpG ODNs are primarily composed of a natural phosphodiester backbone and are the strongest known activator of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) for IFN-α induction.
Recently, cancer immunotherapy using immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as anti-PD-1 antibodies, has gained attention. However, their efficacy is limited to approximately 20%, and the patient population that benefits from this therapy remains small. Vidutolimod, a virus-like particle containing Type A CpG ODNs, is currently in clinical development and is expected to be effective against tumors resistant to anti-PD-1 antibody therapy. However, Vidutolimod must be administered intratumorally. Researchers have developed D35LNP, which is DOTAP based D35(Type A CpG ODN)/lipid complex formed the lipid nanoparticles. D35 LNP provides stable performance of Type A CpG ODN.
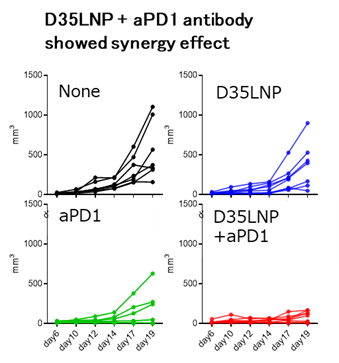
Data
- D35LNP + aPD-1 antibody induce cure of cancer in mice
- D35LNP + radiation also induce cure of cancer in mice
- D35LNP could convert non-responsive to immune therapy responsive tumor
- D35LNP potentially reduce circulating tumor cells medicated metastasis
- D35LNP potentially reduce the development of hereditary cancer
- D35LNP activated Th1 CD4T cells, CD8T cells, and NK cells.
 |
Publication
Munakata L, and Aoshi T et. al., (2019) J Control Release. 313:106-119.
Patent
- JP7520321B (Pending in US, EP, and CN)
Principal Investigator & Academic Institution
Prof. Taiki AOSHI (Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Nagasaki University)
Expectations
TECH MANAGE CORP. is looking for a pharmaceutical company/start-up that is interested in developing cancer drug based on this research project. We also welcome collaborations involving lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) that a company has. Beyond cancer, we are also looking for companies interested in collaborating on therapeutic drug development and R&D related to allergic diseases, infectious diseases, and vaccine adjuvants. Unpublished data and other information regarding this research project can be disclosed under a confidentiality agreement with The University of Osaka, and meetings with researchers can also be arranged.
Project No. TT-05069


