Advantages
- Photo/Environmentally sensitive prodrug development technology
- Could be a repositioning tool to improve selectivity of compounds with side effects
- Processes that can be introduced in addition to imidazole compounds
Background & Technology
In response to the need for more selective expression of bioactivity of small molecule compounds, research in the field of photo-pharmacology on compounds that only become bioactive when irradiated with light is attracting attention. In this field, synthesis of compounds in which a photoreactive protective group that can be removed by the action of light or a group that causes isomerization of the molecular structure by light is introduced into a part of the molecular skeleton of a conventional inhibitor as a photo switching site for controlling biological activity is being considered. However, there were two drawbacks: (1) when the protective group moiety is removed by light, the desorbed molecular moiety is generated as a side reaction product, and (2) the structure of the photoisomerization site is different from that of the original inhibitor, so the bioactivity is weaker than that of the original inhibitor.
As a result of studies to solve the above problem, the inventors discovered that a precursor of an imidazole compound having a 2H-imidazole-2-amine skeleton in its molecular structure generates an imidazole-based bioactive substance in response to external stimuli such as light or the external environment. This technology has already been used to find light-sensitive imidazole bioactive substances in known compounds, and empirical data are being obtained. This method has also been demonstrated to be prodrug-able with compounds other than imidazole compounds, and is expected to be applicable to other compound structures. Based on this, it is possible to make assumptions and conduct empirical evaluations for compounds for which the feasibility of prodrug conversion is to be examined.
Data
B-431542 is a drug candidate substance that is expected to inhibit glioma growth and reduce infectious viral particles, but is known to have solubility and other issues. We synthesized a precursor of this compound and evaluated its photosensitivity and in vitro activity in human mammary carcinoma cells, MDA-MB-231.
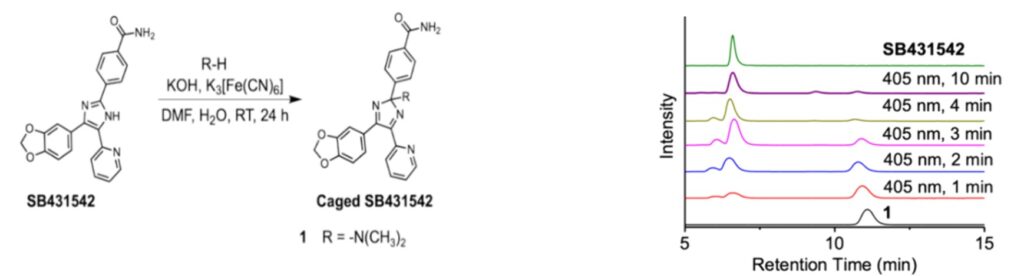 |
Left: 100 mg of SB-431542 was dissolved in DMF, a solution of potassium hydroxide and potassium ferricyanide was added, and the oxidation reaction was stirred at 30°C under nitrogen atmosphere. The resulting organic layer was concentrated and purified by reversed-phase liquid chromatography to yield the SB-431542 precursor 1.
Right:HPLC chromatograms of 1 prodrug after irradiation with 405 nm light for different times. The precursor prodrug of 1 disappears and changes to SB-431542 in an irradiation time-dependent manner.
Patent
JP2023‐72462
Precursors of imidazole bioactive substances and methods of producing imidazole bioactive substances
Publication
Journal of the American Chemical Society 2024 146 (26), 18002-18010
Inventors
Hokkaido University Research Institute for Electronic Science Professor Nobuyuki Tamaoki
Development Phase
Current stage: Evaluation of photosensitivity and in vitro activity of the compounds produced by this prodrugation technology has been completed, and in vivo demonstrations are underway.
Next stage:
1-1) Prodrug synthesis and development of desired compounds
1-2) Development and safety evaluation of obtained prodrugs, optimization evaluation of irradiation light and equipment
2 Clinical development
We are looking for collaborative partners interested in development collaboration for 1 and 2 above. We would be happy to start with a detailed explanation and discussion of our technologies.
Project No. ON-05061


