Advantages
- Inhibits and degrades undruggable RAS
- Can be applied to all RAS (Pan-RAS) except G12C mutant RAS
Current Stage and Key Data
Partnering Model
- Looking for an exclusive license partner for the fusion protein X.
- A feasibility study can be conducted by signing a CDA or MTA for evaluation.
- If further optimization research of the protein is required, a collaborative study can be conducted.
Background and Technology
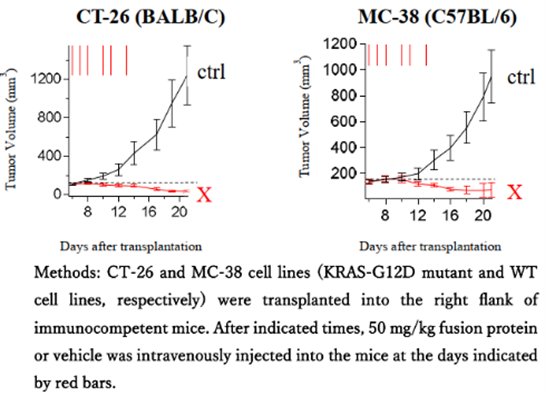
RAS (H-Ras, K-Ras, N-Ras) is a cancer gene that is mutated to an active form in approximately 30% of cancers, and the development of Ras inhibitors has been progressing worldwide. However, many attempts, including small molecule compounds, have failed. In 2021, a small molecule compound (sotorasib) that inhibits G12C mutant Ras was approved by the FDA. The unique feature of sotorasib is that it inhibits the function of Ras by forming a covalent bond with the mutated cysteine residue. However, the remaining approximately 90% of “Non-G12C” mutant Ras is still a difficult target for drug development.
In 2020, we reported that a protein fused with a RAS binding domain (RBD) and a cell membrane-penetrating peptide (CPP) inhibits the binding between RAS and downstream signaling molecules, but the antitumor activity was insufficient (*1). This time, the newly developed protein X fused with a third domain suppressed the function of active RAS and showed high antitumor effects.
Principal Investigator
Ryo Honda (The Graduate School of Drug Discovery and Medical Information Sciences, Gifu University, Tokai National Higher Education and Research System). *Specializes in the design and synthesis of artificial proteins.
Reference
- Paper*1: Nomura et.al., Cell Chemical Biology 28, no. 11 (2021): 1581-1589.
- Patent application*1: WO2022/039026
- New fusion protein X: Paper submitted, patent application filed (unpublished)
Project.BK-04936