Advantages
- No need for difficult procedures such as suturing with clips and applying a protective sheet
- Providing long-lasting mucosal elevation and protection against damage from digestive fluid exposure by staying on the ulcer surface after treatment
- Experimentally-proven efficacy in tissue specimens and living pigs
Background & Technology
Endoscopic submucosal resection (ESD) of early-stage gastrointestinal cancer has become common as an innovative technique that is less physically invasive than surgery and can work as a curative procedure by completely resecting lesions. However, complications such as gastrointestinal perforation that have serious consequences remains unresolved. These risks are particularly high in the duodenum with a thin wall, making the procedure challenging even for experts. Therefore, duodenal ESD is currently performed only at a limited number of institutions.
Insufficient mucosal elevation by local injection makes dissection procedures difficult and occasionally leads to intraoperative perforation. In addition, exposure of post-ESD ulcers to pancreatic fluid with potent digestive enzymes leads to postoperative bleeding and delayed perforation. Intraoperative perforation and delayed perforation have been reported in 1-5% and 0.5% of gastric ESD cases, and 12.8% and 2.2-14.3% of duodenal ESD cases, respectively.
Sodium alginate and hyaluronic acid have been conventionally used as local injection agents. However, because they are liquids, they tend to leak out of the tissue over time, making it difficult to achieve adequate mucosal elevation.
Suturing ulcers with clips, in addition to endoscopic drainage of pancreatic juice, are performed to prevent delayed perforation, but both of these procedures are difficult to perform and occasionally lead to serious consequences. Moreover, although sheets for the protection of tissue defects are applied clinically, but it is not easy to release and fix the sheets accurately using an endoscope.
Therefore, we invented a novel local injectable that stays in the submucosa for an extended period. The agent contains three solutions: a first solution of calcium carbonate suspended in water-soluble sodium alginate, a second solution with water-soluble chitosan salt adjusted to acidity, and a third solution with a highly water-soluble calcium ion donor.
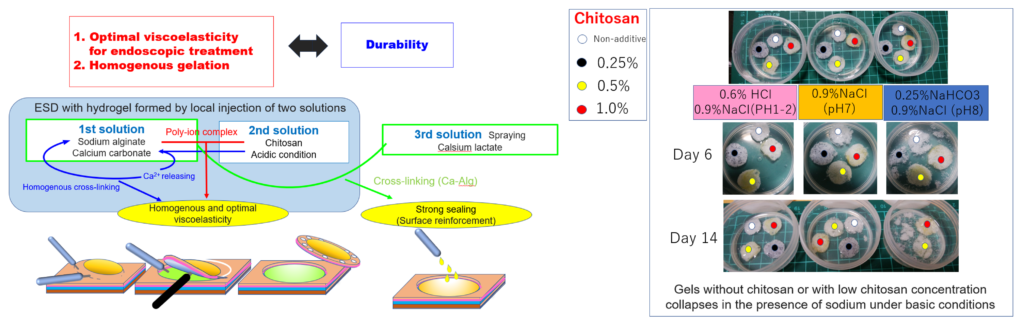 |
By adjusting these solutions to the appropriate concentration ratio and injecting them locally at the appropriate timing, they react within the submucosal tissue to form a homogenous hydrogel, achieving effective mucosal elevation that cannot be achieved with conventional products. Furthermore, after ESD, this hydrogel stays in the submucosa and coats the ulcer, providing anti-ulcer and wound healing effects. The effectiveness of this material has been demonstrated in living porcine gastric and duodenal ESD models. This material elevated the mucosa better than only sodium alginate did and remained on the surface of the ulcer for an extended period, with the help of the submucosal fibrous connective tissue acting as a supporting tissue to hold the gel in place.
Furthermore, experiments using living pigs confirmed that the novel hydrogel can be applied to the closure of anastomotic leakage after gastrointestinal surgery. By forming a gel in the tissue surrounding the leakage through local injection of reagents, the tissue surrounding the leakage becomes swollen, making the leakage site adherent and eventually leading to permanent closure by fibrotic adhesion. The use of this hydrogel will be valuable as a novel endoscopic treatment method in fields in which conservative treatment is ineffective.
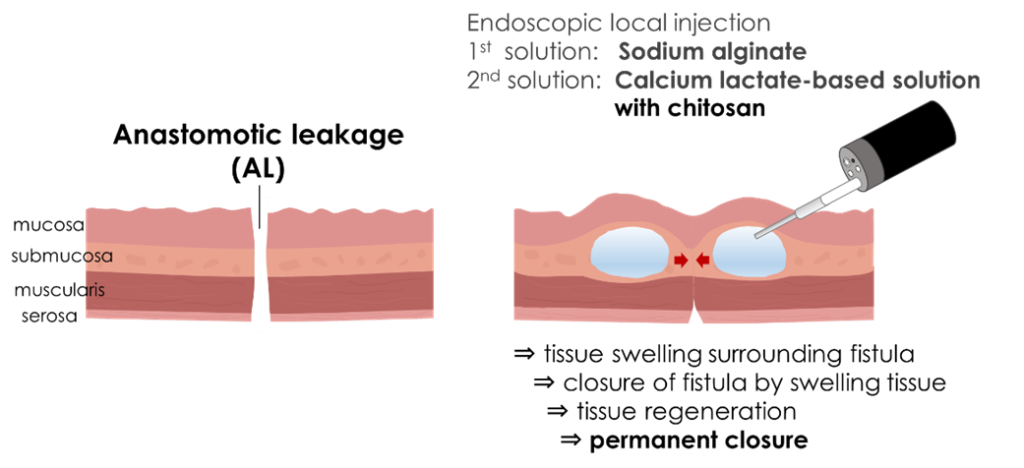 |
Researcher
Keiko Yamamoto, Division of Endoscopy, Hokkaido University Hospital
Yusuke Watanabe, Clinical Research and Medical Innovation Center, Institute of Health Science Innovation for Medical Care, Hokkaido University Hospital
Takayuki Kurokawa, Department of Advanced Transdisciplinary Sciences, Faculty of Advanced Life Science, Hokkaido University
Patent
Publication (international phase)
Publication
Yusuke et al., “Novel endoscopic management of gastroenterological anastomosis leakage by injecting gel-forming solutions: an experimental animal study”, Surg Endosc. 2023 Oct;37(10):8029-8034.
doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10243-2. Epub 2023 Jul 19.
Development Phase
Current stage: Proof of concept and performance of this material using tissue fragments and living organisms (pigs) is complete.
Next stage:
(i) Examination and verification of effects on surrounding tissues, etc. (ongoing).
(ii) Establishment of optimal protocols according to the purpose of use and case.
(iii) Demonstration for obtaining medical approval
We are looking for partner companies interested in introducing the technology and joint development for the practical application and development of the above.
We would be happy to provide a detailed explanation of this technology and have a consultation regarding the technology at first.
Project.ON-03769b


