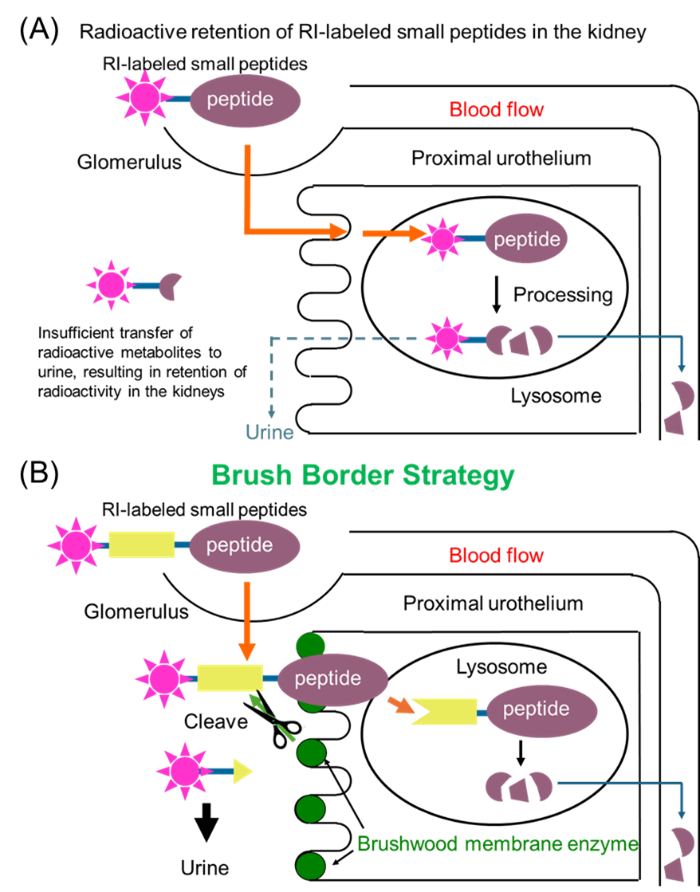
Advantage and Core Benefit
- Rapid clearance after administration and is rapidly excreted in the urine without retention in the kidneys.
- Target tissues close to the kidney can also be imaged.
Background and Technology
RI-labeled small molecule antibody (67Ga-NOTA-MVK-Fab) was prepared by placing MVK (Met-Val-Lys), a cleavage sequence of renal brush border membrane enzyme, between the NOTA-chelated RI-labeled molecule (67Ga-NOTA) and the Fab fragment of the small molecule antibody. The results of administration studies in mice confirmed that the RI-labeled molecular portion (67Ga-NOTA-Met) cleaved from 67Ga-NOTA-MVK-Fab was excreted as urine without being reabsorbed by the kidney cells. Furthermore, it was possible to clearly image cancers located close to the kidney. In addition, the inventors tried several enzyme recognition sequences and found an FGK (Phe-Gly-Lys) sequence that further improved accumulation in mouse kidneys and produced 67Ga-NOTA-FGK-Fab.
 |
Data
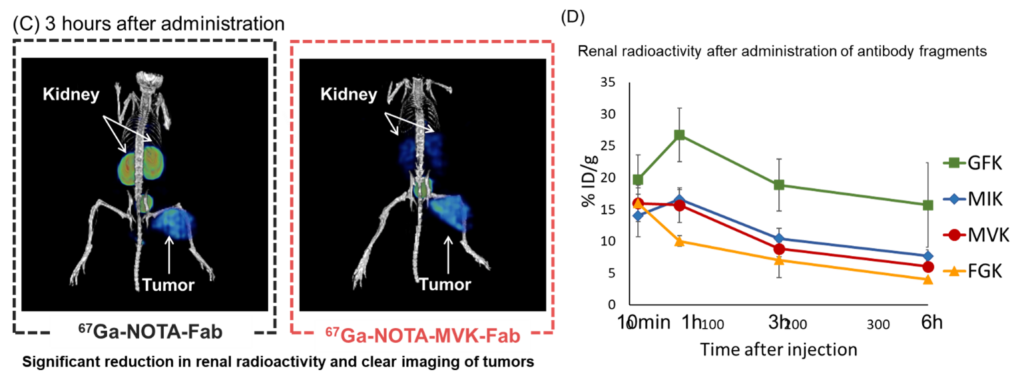
- When mice were administered RI-labeled Fab and observed by SPECT/CT imaging, RI signals were observed in the tumor and kidney for 67Ga-NOTA-Fab, while 67Ga-NOTA-MVK-Fab showed only tumor and no renal accumulation.
- When RI-labeled antibodies containing different enzyme recognition sequences (MVK/FGK/GFK/MIK) were administered, 67Ga-NOTA-FGK-Fab showed the lowest renal radioactivity.
Patent & Publication
PCT/JP2017/007875, US10960089B, EP3424940A, JP6966741B, CN108699108B, PCT/JP2023/046536
Researcher
Dr Tomoya Uehara (Chiba University Laboratory of Molecular Imaging Pharmaceutics)
Expectations
We are interested in partnering with companies that are developing radiopharmaceuticals to commercialize this invention through licensing. In particular, we welcome joint development with companies developing radiopharmaceuticals using copper isotopes and chelating agents such as NOTA.
Project.WL-04832