Advantage and Core Benefit
- Mechanism induces activation of immune cells rather than inhibition of inhibitory receptors such as PD-1 and CTLA4
- Expected to enhance the effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors when used in combination
Background and Technology
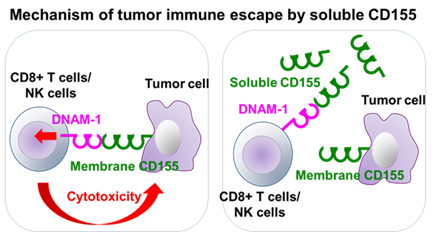 |
To develop cancer immunotherapy, it is important to clarify the immune surveillance against tumor cells by the immune system and the escape mechanisms from immune surveillance by tumor cells.
Inventors have previously found that the T-cell activating receptor DNAM-1 is responsible for immune surveillance against tumor cells by binding to CD155 on tumor cells and killing them.
Unlike mouse CD155, a soluble form of human CD155 exists due to a splicing variant that lacks a transmembrane site. When a soluble CD155-producing cancer cell line (sCD155-MethA) was generated and transferred into mice, rapid tumor growth and reduced survival were observed compared to a non-producing cancer cell line (Mock-MethA). On the other hand, transfer of these cell lines into DNAM-1 gene-deficient mice showed no difference in carcinogenicity and survival, indicating that tumor cells escape immune surveillance by DNAM-1 by producing sCD155. Furthermore, soluble CD155-producing cancer cell lines were shown to attenuate the effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Specific antibodies against sCD155 were established by the inventors, and the anti-tumor effect of these antibodies on soluble CD155-producing cancer cell lines was demonstrated. The anti-tumor effect of this antibody was mediated by activation of CD8-positive T cells.
Data
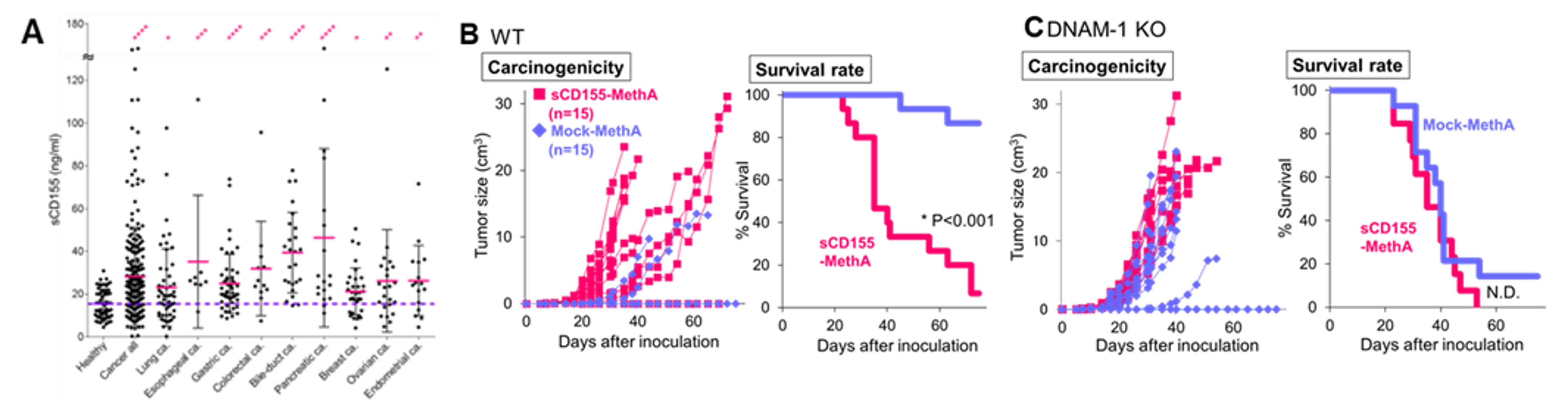 |
- Values of sCD155 in serum of cancer patients and healthy subjects (A). In all cancer types analyzed, sCD155 in cancer patient serum was significantly higher than in healthy controls.
- Carcinogenicity and survival of sCD155-producing tumor lines (sCD155-MethA) and control tumor lines (Mock-MethA) when transferred into wild-type (B) DNAM-1 KO mice (C)
Patent & Publication
JPB 5850508, JPB 5686361, JPB 5995117
PLOS ONE (DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152982),
J Exp Med (doi.org/10.1084/jem.20191290)
Researcher
Dr. Kazuko Shibuya, Dr. Akira Shibuya (University of Tsukuba)
Expectations
We are looking for companies that are interested in developing therapeutics based on specific antibodies against sCD155 established by the inventor. In particular, we are looking to collaborate with companies that have antibody technology that improves the activity of specific antibodies to remove sCD155. Data on the established antibodies can be disclosed under a CDA.
Project No. WL-02746


