Advantage and Core Benefit
- It promoted bone formation through the induction of osteoblast-specific expression of Runx2 but showed no effect on cartilage.
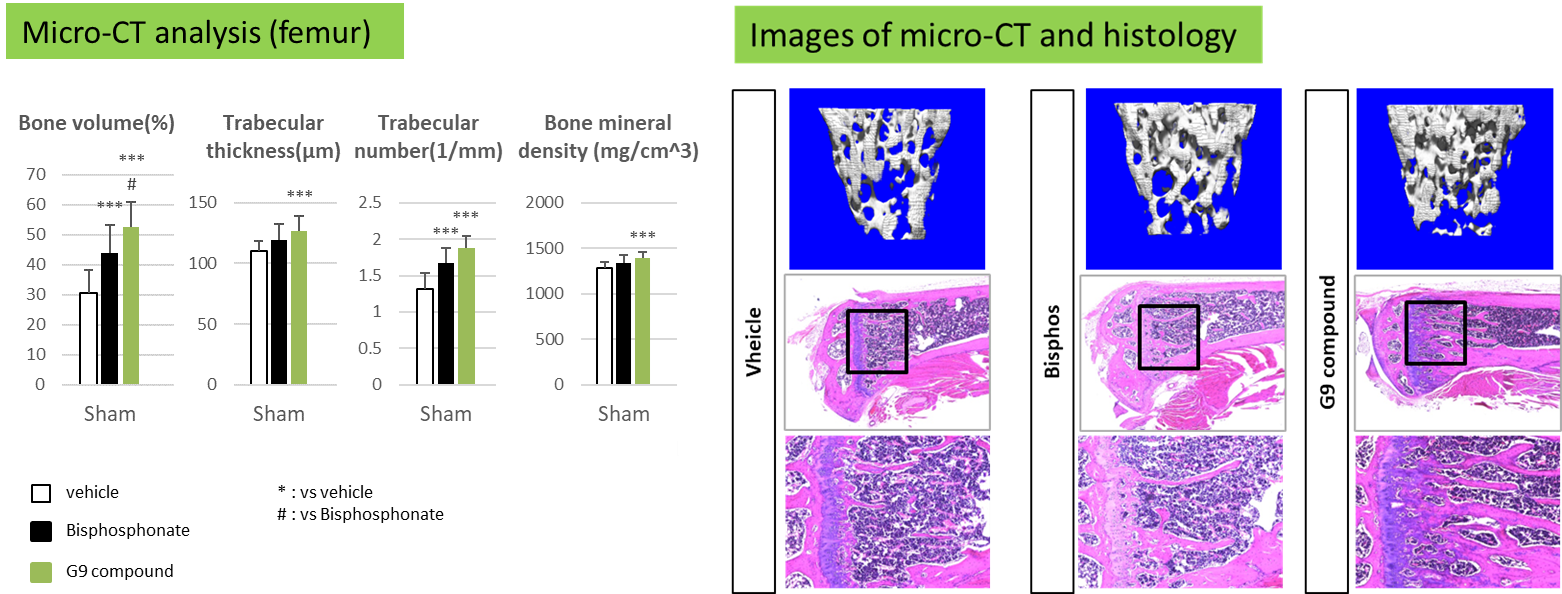
- In vivo experiments showed a significant increase in bone volume and other parameters compared to Bisphosphonate. Bone histomorphometry confirmed the promoted osteogenesis.
- The researcher has extensive knowledge of the mechanisms of bone and cartilage formation and the search for therapeutic agents.
Background and Technology
The number of osteoporosis patients is increasing in an aging society. However, the inhibitors of bone resorption such as bisphosphonates have problems like osteonecrosis of the jaw, poor bone quality, and suppression of bone formation, while the use of injectable parathyroid hormone and anti-sclerostin antibody, which promote bone formation, is limited to 1-2 years due to the risks of osteosarcoma and cardiovascular diseases, respectively.
The researcher has for many years worked on the transcription factor Runx2, which is essential for the differentiation of osteoblasts and chondrocytes, to understand the mechanisms of bone and cartilage formation and to develop therapeutic agents, and has discovered a novel compound “G9”, which promotes bone formation. Runx2 promotes osteogenesis while inducing chondrocyte maturation and destroying cartilage. However, G9 has a specific effect on osteoblasts but no effect on cartilage.
In vivo experiments showed a significant increase in bone volume and other parameters in the femoral trabecular bone of the sham group, compared to Bisphosphonate. In addition, bone histomorphometry in ovariectomized mice confirmed promoted bone formation.
 |
Patent
Pending
Researcher
Toshihisa KOMORI (Nagasaki University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Professor)
Expectations
We are looking for a company to develop a novel osteogenesis-promoting drug based on this candidate compound.
Project No: HK-04315


