Advantage and Core Benefit
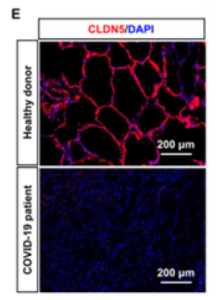
- Reduced CLDN5 expression and vascular barrier disruption were observed in the lungs of COVID-19-infected patients
- Fluvastatin, an existing medicine that enhances CLDN5 expression, suppresses the disruption of the vascular barrier
- CLDN5 levels in blood were found to be decreased in critically ill patients, suggesting that CLDN5 may be a biomarker for the severity of illness.
- Screening of new small molecules using an original CLDN5 binding assay system
- Evaluation of new candidate compounds using an original model assay system for the disruption of the vascular barrier
- Already identified several antibodies and small molecules that restraint the vascular barrier
Background and Technology
Claudin-5 (CLDN5) is a cellular tight junction molecule, expressed in tight junctions such as vascular endothelial cells, mainly in microvascular endothelial cells of the lung and brain.
The researchers in Japanese universities found that SARS-CoV-2 disrupts the vascular barrier by suppressing CLDN5 expression on vascular endothelial cells and attenuating adhesion between them, using a “respiratory tract chip”, an original model system of vascular barrier disruption. We found that CLDN5 expression was reduced in the lungs of patients with COVID-19 infection (see the right figure). Furthermore, Increasing CLDN5 expression in vascular endothelial cells by gene transfer or small molecule drug (fluvastatin) can suppress vascular endothelial barrier disruption caused by SARS-CoV-2. Based on these facts, the researchers propose that compounds targeting CLDN5 are a potential treatment for the severity and post-illness symptoms of infections, including COVID-19. We have several antibodies and small molecules that regulate the function and expression of CLDN5. In addition, research is underway on technologies such as increasing the permeability of the blood-brain barrier to deliver drugs into the brain, inhibiting the disruption of the vascular barrier caused by central nervous system disease.
 |
Papers
- Hashimoto et al., Science Advances (2022) 8(38)
- Hashimoto et al., Biol Pharm Bull. (2021) 44(10):1380-1390
Researcher
Associate professor
Yoshiaki OKADA (The University of Osaka)
Expectations
This study has confirmed the disruption of the vascular barrier by COVID-19 in respiratory tract chips and the lungs of COVID-19 patients. And CLDN5 enhancement by a small molecule is a promising strategy to treat for severity and post-illness symptoms of infections, including COVID-19. We are looking for collaborative partners to develop therapeutics and biomarker measurement systems based on this therapeutic concept using our proprietary assays and tools.
Project No: DA-01670c


