Advantages
- Novel size analyzing method based on different principle from existing method.
- This technology enables short-time analysis than pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE).
Background and Technology
Pulsed-field electrophoresis (PFGE) is standard gel electrophoresis, which has been widely utilized in DNA separation for various genotyping and sequencing application. However, DNA separation by PFGE takes 1 – 2 days. Therefore, there is a growing demand for more rapid methods for the separation of large DNA molecules.
Electrophoresis using micro/nanofluidic devices, based on size exclusion chromatography (SEC) has been developed for DNA separation. However, this separation principle is based on the difference between the diffusion coefficients of Brownian motion of molecules. Therefore, this method needs a large amount of samples and passage time of all samples through micro/nanofluidics.
In this study, the researchers developed a new method based on measuring the relaxation time of DNA molecules. It was reported that the relaxation time depends on the number of molecules. Therefore, this method is expected to lead to offering fast, accurate high-resolution separation and analysis and requires very small amounts of sample for analysis.
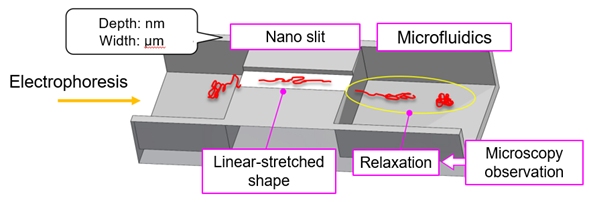
For measuring the relaxation time, the researchers propose the device, which have nano slit and microfluidics. A DNA molecule migrates into the microfluidics with its random-coiled shape due to its electrophoresis by applied voltage and it is deformed to a linear-stretched shape to enter the nanogap. The measurement of relaxation time through single-molecule analysis is detected by observing using an optical microscope when it passes the nanogap.
 |
Patent
Pending
Researcher
Shintaro Itoh (Nagoya university)
Development Stage and Expectations
- In this study, the researchers achieved the separation of large DNA molecules (a 48.5-kbp fragment of λ DNA and a 166-kbp fragment of T4 DNA) utilizing the prototype device.
- This technology is expected to apply the identification of microbial strains of bacteria, karyotyping of yeast, cloning of large DNA, and purification of nucleic acid drugs. it is necessary to demonstrate this technology in these applications.
- Further development of micro- and nano-fluidic devices.
We are looking for partners interested in the above-mentioned research and development. We can provide additional information and set up meetings with researchers.
Project No. TT-04091


