Advantages
- Direct measurement of T-cell cancer cytotoxic activity.
- A measurement technique using peripheral blood of the patient, which is relatively minimally invasive and inexpensive.
Technology Overview & Background
While some immune checkpoint inhibitors have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in enhancing T-cell anti-tumor immune responses, improving the response rate remains a key challenge. To address this, clinical development efforts are exploring combination therapies alongside patient stratification using companion diagnostics. For example, pembrolizumab, a treatment for non-small cell lung cancer, has been approved in conjunction with a diagnostic test that detects PD-L1 positivity in lung cancer tissue. As a result, there is a growing need for diagnostic methods with higher sensitivity and specificity that can more accurately and easily predict therapeutic efficacy.
The researcher identified a potential method for predicting the therapeutic efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibodies by measuring the T-cell cytotoxic activity against cancer cell lines in the peripheral blood of cancer patients before treatment begins. This approach utilizes BiTE (Bispecific T-cell Engager), a molecule that simultaneously binds to T cells and cancer cells. He named this liquid biopsy method Peripheral T-cell Cytotoxicity (PeriCyto). Because it requires only a peripheral blood sample, it is a relatively minimally invasive test. Additionally, it provides valuable insights as a functional assay that directly measures the cancer-killing activity of T cells—a crucial mechanism of action in cancer immunotherapy.
Data
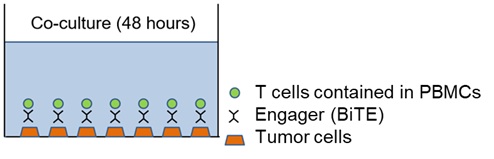
- PBMCs are collected from peripheral blood of patients planning to be treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors and co-cultured with cancer cell lines for 2 days in the presence of BiTE (EphA2/CD3 recognition) as shown in Figure 1, and then cancer cytotoxic activity is measured.
Figure 1. Measurement overview of PeriCyto
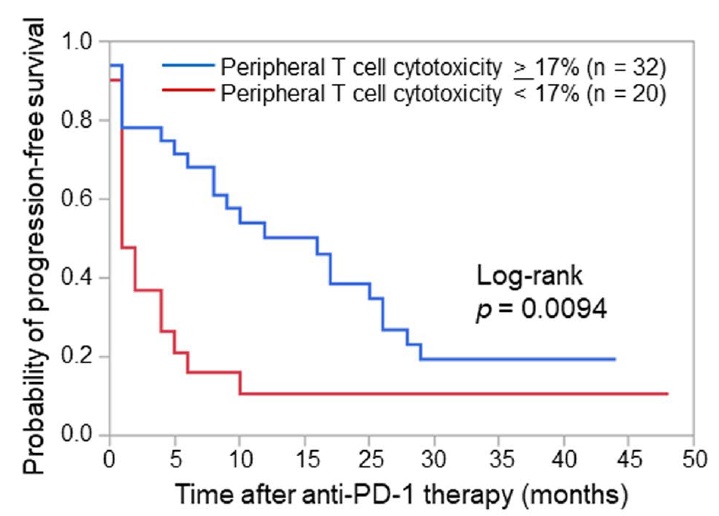
- The usefulness of PeriCyto technology as a predictive method of anti-PD-1 antibody treatment efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) was confirmed, and significantly prolonged progression-free survival was observed in the high PeriCyto group as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. The progression-free survival of NSCLC patients for the first-line or later treatments according to PeriCyto levels
- Similar results were also obtained for adenocarcinoma, melanoma, mesothelioma, and urothelial carcinoma, suggesting that PeriCyto may be useful in many solid tumors.
[DOI] https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2023-SITC2023.0048
Publication(s)
K. Iwahori, et al. “Peripheral T cell cytotoxicity predicts T cell function in the tumor microenvironment.” Scientific Reports volume 9, Article number: 2636 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39345-5
K. Iwahori, et al. “Peripheral T cell cytotoxicity predicts the efficacy of anti‑PD‑1 therapy for advanced non‑small cell lung cancer patients.” Scientific Reports volume 12, Article number: 17461 (2022).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-22356-0
Patent(s)
PCT/JP2018/024770
Registered in the countries listed below; all can be licensed from The University of Osaka.
– (CN) ZL201880043689.2 / Issued
– (EP) 3647433 / Issued and maintained in France (FR), Germany (DE) and the UK (GB)
– (JP) 6930760 / Issued
– (US) Granted
Principal Investigator & Institution
Kota IWAHORI, MD, PhD
(General Manager, Dept. of Cancer Immunotherapy, Osaka International Cancer Institute)
Expectations
On behalf of The University of Osaka, TECH MANAGE is seeking partners interested in utilizing PeriCyto technology as a companion diagnostic method in the development and approval process of immune checkpoint inhibitors. This project is already in progress, alongside collaborations with companies interested in supplying BiTE and PeriCyto assays.
We would be happy to arrange a meeting with our researcher and other parties. We appreciate your consideration of this proposal and would greatly value your feedback regarding your company’s potential interest in this technology. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
Project Code: JT-03945