Advantages
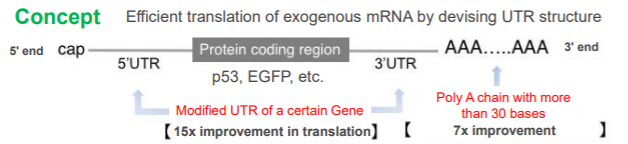
- Activates translation by using the 5′ and 3′ UTRs of a certain gene
- By optimizing the UTR structure, we achieved a 15-fold increase in efficiency compared to conventional technology*.
(*compared with beta-globin UTR standard) - Translation efficiency was confirmed with exogenous mRNAs such as p53 ( Lower figure) and EGFP.
- No cell specificity, widely applicable to HeLa, HEK293 cells, etc. Can be applied to improve expression efficiency of mRNA drugs
 |
Background and Technology
The mRNA medicine is attracting attention as a gene therapy that does not require the use of viral vectors and has a low risk of carcinogenesis. However, the instability of artificial mRNA in the cell has been a major problem.
The inventors have been studying the mechanism of degradation and stabilization of artificial mRNA in cells, and have focused on the mechanism of increasing the translation efficiency of RNA.
By incorporating the untranslated region (UTR) of a particular gene into the artificial mRNA, it was shown that the translation efficiency of the protein in the transduced cell was improved.
Application
(1) Cancer immunotherapy
(2) Generation of iPS cells
(3) Gene therapy and treatment of viral diseases
(4) Replacement therapy for disease-causing genes
(5) RNA Vaccine
Patent
Pending in PCT
Expectation
- Licensing of this technology for the development of mRNA drugs and RNA vaccines (for Pharmaceutical company, Biotech)
- Internal use as a research and development tool
Product No. WL-03105


