Advantages
➢ High affinity and specificity (Kd = 8nM)
➢ One-to-one bond (avidin is a tetramer, so avidin-biotin system forms one-to-many bond)
➢ HPPU dose not exist in nature (biotin is a natural substance and exists in the living body, so it becomes noise)
 |
Background
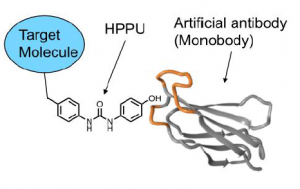
Proteins that specifically bind to small molecule ligands play an important role in biological research. The most common are biotin-avidin interactions. However, since avidin is a tetramer, it is difficult to bind the biotinylated target molecule to avidin on a “one-to-one” basis. In addition, since biotin is a natural compound, biotin and biotinylated proteins existing in the living body also bind to avidin. From this point of view, it is required to develop a protein that binds to a non-natural small molecule in a “one-to-one” relationship and has high affinity and specificity.
A protein (Monobody) candidate that specifically binds to 1- (4-hydroxyphenyl) -3-phenylurea (HPPU), which is an artificially designed small molecule ligand, was selected from an artificial antibody library which has a diversity of 1013 by our original TRAP system. The protein was further optimized.
Data
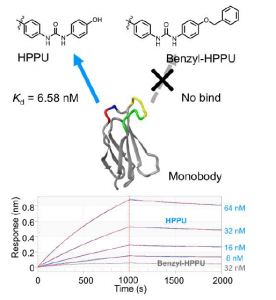
- This artificial antibody has a high affinity for HPPU (Kd = 6.6 nM).
- This artificial antibody does not bind to HPPU with a benzyl group.
 |
Patent
Patent pending (unpublished)
Researcher
Hitoshi MURAKAMI Ph.D., Professor (Tokai National Higher Education and Research System, Nagoya University Graduate School of Engineering)
Goals
Looking for collaborative partner companies aiming to commercialize reagents and kits for research of this technology
➢ At the current research stage, HPPU-Monobody system has been constructed, and applied research for cell analysis is underway.
➢ Feasibility study with CDA / MTA
➢ Development and Commercialization (after the paper is published) with royalty bearing license
Product No. BK-03583


