Abstract
- GREB1 is one of the key regulators of cell proliferation and has been shown experimentally to be an effective therapeutic target for malignant melanoma and hepatoblastoma.
- Arl4c is overexpressed in several solid tumors and has been detected as an important factor in cancer cell motility, invasion, and proliferation, confirming that treatment with ASO targeting ARL4C gene is effective against lung adenocarcinoma and pancreatic cancer as well as liver metastatic foci of colon cancer.
Advantages
- ASOs targeting GREB1 or ARL4C genes can reduce and inhibit tumor growth.
- Combined with tumor lesion integration techniques and effective nuclear delivery techniques, the effectiveness of these ASOs can be further enhanced.
Technology Overview & Background
Researchers focus on comprehensively understanding the molecular mechanisms of Wnt signaling, regulated with other pathways such as TGF-β, EGF, and Hedgehog signaling.
1. GREB1 (Growth Regulating Estrogen Receptor Binding 1)
Hepatoblastoma is a rare form of liver cancer, affecting just a few individuals per million, it is the leading cause of liver cancer in infants and young children. Researchers identified GREB1 as an unknown target gene for Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Analysis of publicly available data sets showed that GREB1 was overexpressed in tumor lesions in more than 90% of hepatoblastoma tissues. The region-specific expression pattern of GREB1 in hepatoblastoma tended to be positively correlated with the accumulation of β-catenin.
Overexpression in other tumor patients was also identified in the dataset, and more recently, their team found that one isoform of GREB1 is specifically expressed in melanocytic melanoma.
2. Arl4c (ADP-ribosylation factor-like 4c)
Arl4c was identified as a small molecule GTP-binding protein, which is expressed by Wnt and EGF signaling, plays an important role in tubulogenesis of cultured cells and the ureters.
Researchers of this project found that expression of the mRNA of ARL4C is highly expressed in some tumor lesions, for example, colon cancer and lung adenocarcinomas, where genetic alterations of Wnt/β-catenin and EGF/Ras pathways are frequently observed, and Arl4c expression promoted migration, invasion, and proliferation of cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that Arl4c was not observed in non-tumor regions, however, Arl4c is overexpressed in tumor lesions in 70-80% of lung and tongue squamous cell carcinoma.
Data / Methods
Researchers investigated the suppressing tumor formation effect and inhibiting growth effect in vivo study using GREB1– and ARL4C-targeted AmNA-modified ASOs.
* AmNA-modified ASOs: In these projects, Amido-bridged nucleic acid (AmNA) was used to improve nuclease resistance and decrease hepatotoxicity.
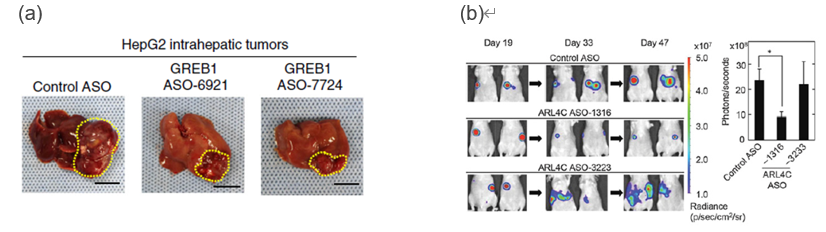
- The therapeutic effect of GREB1 ASO was investigated by implantation of HepG2 cells into the liver of nude mice. In ASO treated mice, suppressed tumor formation compared with control.
See Fig. (a). - The therapeutic effect of ARL4C ASO was investigated by metastatic colorectal cancer in the liver (implantation of HCT116 cells into spleen). ARL4C ASO inhibited the growth of tumor.
See Fig. (b).
For more detailed data and more experiments on the effects on other solid tumors, see related papers below.
Publications
GREB1 Project:
- Matsumoto S, et al., Nat Commun. (2019) 10(1):3882.
- Matsumoto S, et al., Cancer Res. (2023) 83(14):2312-2327. # hepatocellular carcinoma
- Shinzawa K, et al., Oncogene. (2023) 42(42):3142-3156. # melanoma
Alr4c Project:
- Matsumoto S, et al., EMBO J. (2014) 33(7):702-718.
- Fujii S, et al., Oncogene (2015) 34, 4834-4844.
- Matsumoto S, et al., J Biochem. (2017) 161(1):27-35.
- Harada T, et al., Mol Cancer Ther. (2019) 18(3):602-612. # liver tumor
- Kimura K, et al., Cancer Sci. (2020) 111(3):951-961. # lung adenocarcinoma
- Harada A, et al., eLife (2021) 10:e66721. # pancreatic cancer
Patents
GREB1 Project:
PCT/JP2020/020274
→ Japan (pend.) pub. # JPWO2020/235671(A1)
→ U.S. (Granted) pub. # US2022/0249538(A1)
Arl4c Project:
PCT/JP2019/034746
→ EPO (pend.) pub. # EP3848460(A4)
→ Japan (Issued) pub. # JP7396577(B2)
→ U.S. (Issued) pub. # US12,071,624(B1)
Principal Investigator
Akira Kikuchi, MD, PhD
Specially Appointed Professor, CiDER, The University of Osaka (Japan)
Expectations
Tech Manage is now looking for companies to collaborate with the PI and develop this technology further under the licensing of the related patent(s) described above. You can also consider joint research using the invention, providing know-how under a confidentiality agreement (CDA), or setting up evaluation or licensing options for a certain period.
Project IDs: JT-01084 (Arl4c) & JT-02374 (GREB1)