Advantage
- It has high social needs for diagnosis of POI that affects 1% of all women.
- It is expected potential market because this method could be applied to periodic health examination for woman when this biomarker be authorized as risk diagnosing for POI.
- It can be bombinated to sampling device for Menstrual blood.
Background and Technology
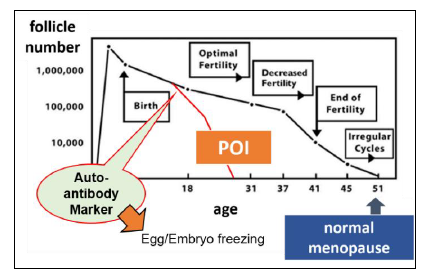
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) happens when a woman’s ovaries stop working normally before she is 40. The prevalence of POI is estimated at 1% in the general population. Once diagnosed as high risk population of POI, she could select the options such as external fertilization, egg cells or embryo freezing for pregnancy. So is has high social needs for risk diagnosis of POI. Nevertheless it has presumed the relation of autoimmune diseases of the thyroid and/or adrenal glands with POI in some patients, the pathogenesis of the disease in most cases remains unexplained.
The inventors identified the ovarian molecules POTEF and POTEE as the target of autoantibody, by proteome analysis for serum from POI patient who also has autoantibody reacting to thyroid tissue. The detection system for the autoantibody has been established with recombinant protein of POTEF and POTEE. The inventors has a plan to trace some women in a group of consented student (>500) by measuring anti-POTEF or -POTEE antibody in their serum.
Data
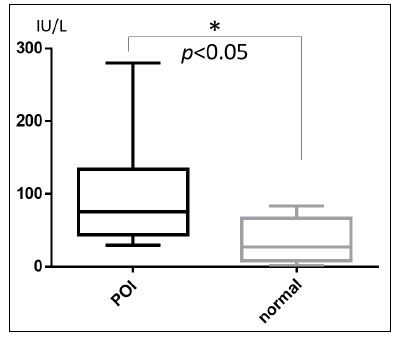
The level of anti-POTEF antibody was significantly higher in POI group than healthy control. The vertical axis: a calculated concentration which is compensated by reference POI serum value (50-fold dilution) as 50 IU/L.
Patent
Pending
Researchers
Dr. Satoko Osuka and Dr. Nobuyoshi Takasaki (Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine)
Expectations
We look for a company who commercialize the POI diagnosis technology under license.
Product No:WL-03205