Advantage and Core Benefit
- Higher sensitivity than conventional screening test and blood biomarker like CEA and CA19-9
- Distinguishable between gastric cancer, esophageal cancer and colorectal cancer
- Minimally invasive and easy to collect
Background and Technology
Gastric or colorectal endoscopy and biopsy is gold standard for diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancer. However, it is not applicable for early examination and screening because of high invasive and high cost. Screening is looking for cancer and the risk before a person has any symptoms. This can help find cancer at an early stage. When abnormal tissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer may have begun to spread.
Based on fair evidence, conventional screening with barium-meal photofluorography, fecal occult blood test or serum pepsinogen (CEA, CA19-9) would not result in a decrease in mortality from gastrointestinal cancer. Novel screening markers with minimally invasive are required.
We analyzed urine sample from healthy people and relatively early stage gastric cancer, esophageal cancer and colorectal cancer patients and identified specific miRNAs expressed in the each cancer patient urine. We found that these miRNAs in urine indicated higher sensitivity for gastrointestinal cancer than the conventional biomarkers in blood. We think that the urine miRNAs can be biomarkers for gastrointestinal cancer screening.
Data
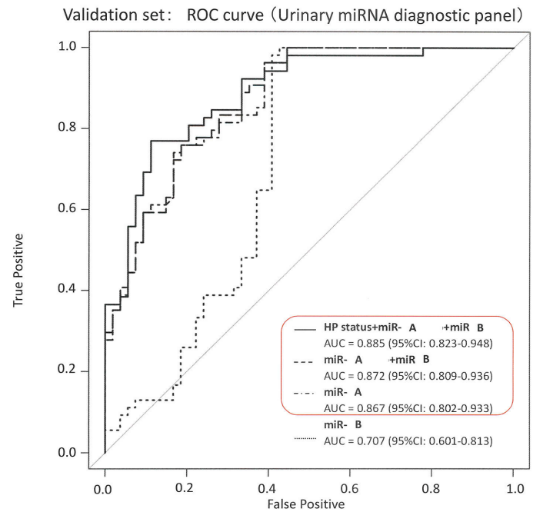
- Urinary miRNA biomarkers were identified by using miRNA array analysis with healthy volunteers and each cancer patients
- The identified biomarkers were validated by accuracy measurement of urinary miRNAs panel with another healthy volunteer and each cancer patient groups. Right figure shows validation data for gastric cancer.
- The identified miRNAs were also changed in tumor tissue and blood.
Patent
Pending, unpublished
Researcher
Takaya SHIMURA (Nagoya City University)
Expectations
We are looking for a partner company to develop this technology as screening test for early stage gastrointestinal cancer patients under a royalty bearing license agreement with the university.
Product No : BK-02718